Find rings pro
Added in version 3.14.0.
This modifier identifies and visualizes ring structures formed by bonds between particles.
You can either load the bonds needed by this modifier from a file or generate them within OVITO using the Create bonds modifier.
Definition of a ring
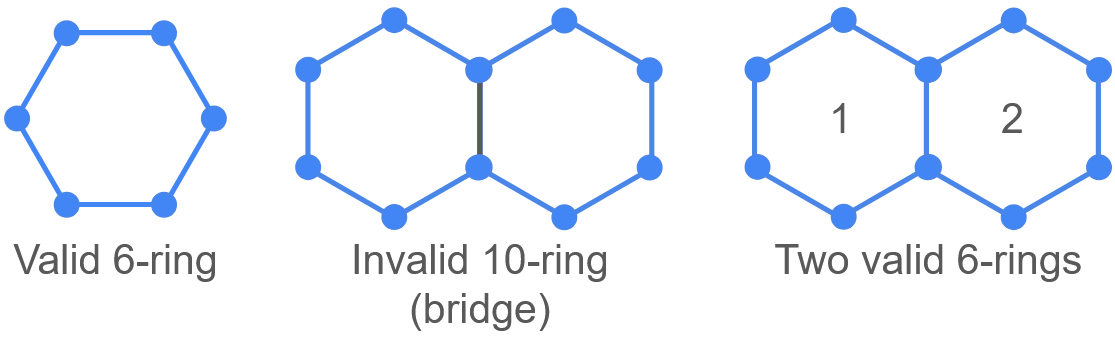
A ring is a closed path made of bonds. Rings identified by the algorithm must not contain bridges. This means the shortest path between any two particles within the same ring must be a section of the same ring, i.e., the path cannot be a shortcut. This is shown in the following schematic. The 10-ring is not a valid ring, because a shortcut exists between two of its atoms. Instead, the modifier finds two 6-rings.
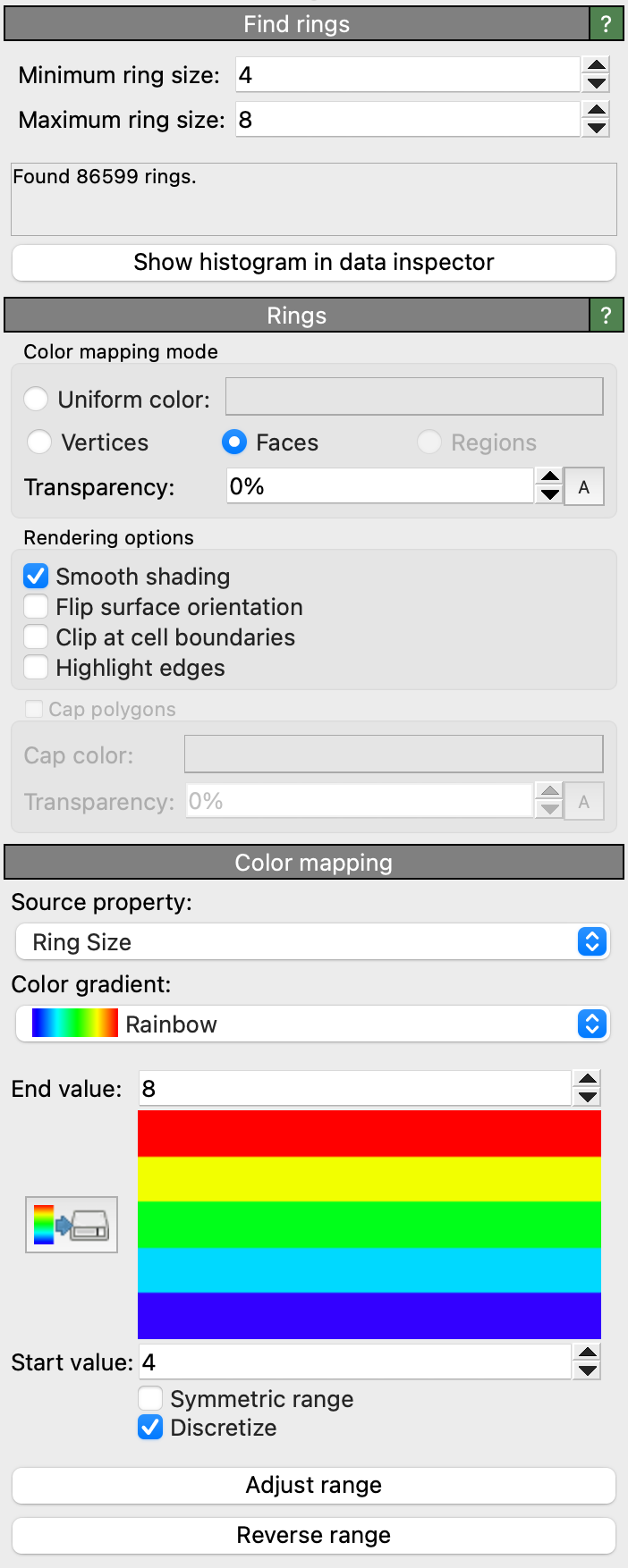
The modifier has two parameters specifying the rings to be identified:
- Minimum ring size
Minimum size of the rings identified by the modifier (inclusive). It must be at least 3.
- Maximum ring size
Maximum size of the rings identified by the modifier (inclusive). It must be greater than the minimum ring size and at most 36, the maximum ring size supported by this modifier.
Outputs
- List of rings
For each ring size \(N\) in the specified range, the modifier outputs a data table, named
N-rings, listing each detected ring of that size. Each row in the table contains the 0-based indices of the particles forming a ring; the first and last particles listed are implicitly connected.- Ring size histogram
Additionally, a data table with the histogram of ring sizes is produced, summarizing the distribution. You can open this histogram by clicking Show histogram in data inspector.
- Ring polygons
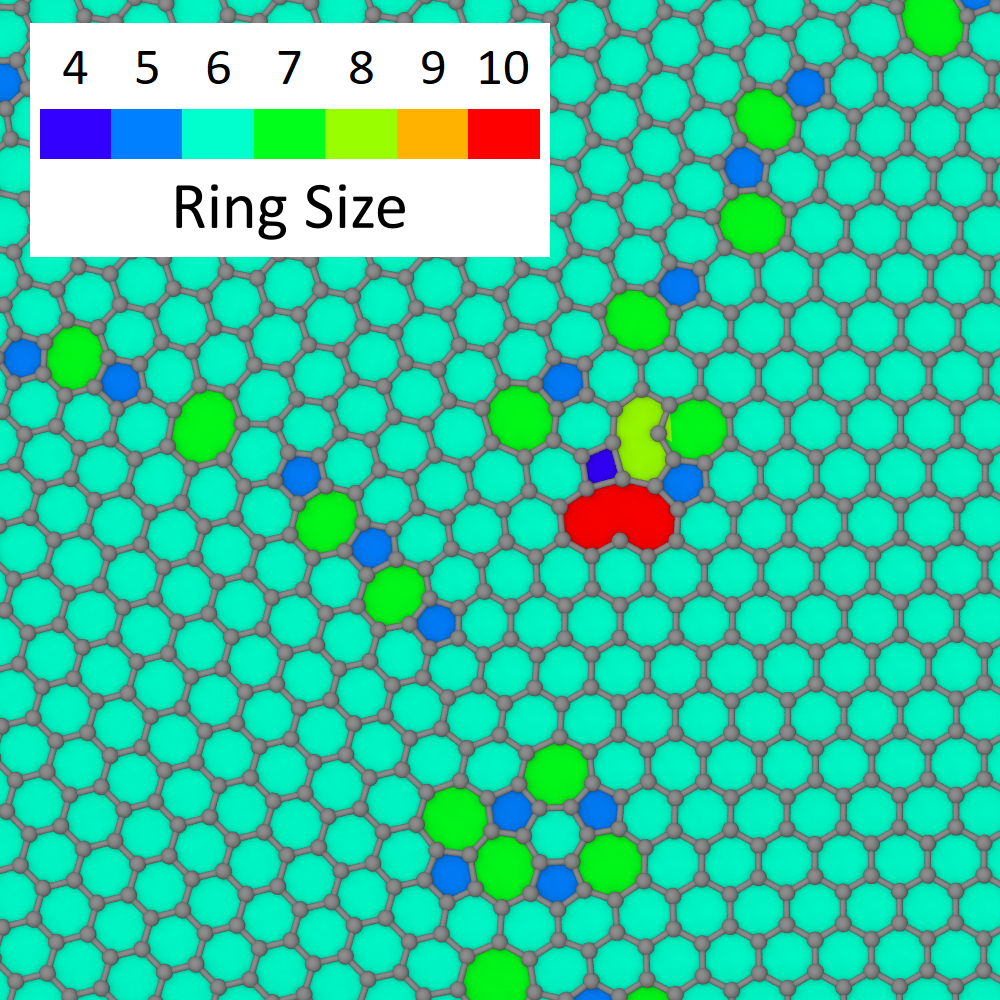
The modifier also creates a surface mesh to visualize the rings as polygons. You can adjust the color mapping of the Surface mesh visual element to represent the size of each ring with a color, as in the example below.
See also
ovito.modifiers.FindRingsModifier (Python API)